Use Case | Cyber Risk Intelligence in the Supply Chain – Identify the Gaps Before They Escalate
In the automotive industry, The supply chain is structured typically in Tier1, Tier2,…
Security Supply Chain Management is getting more important as their biggest blind spot is the SW supply chain. See two boxes.
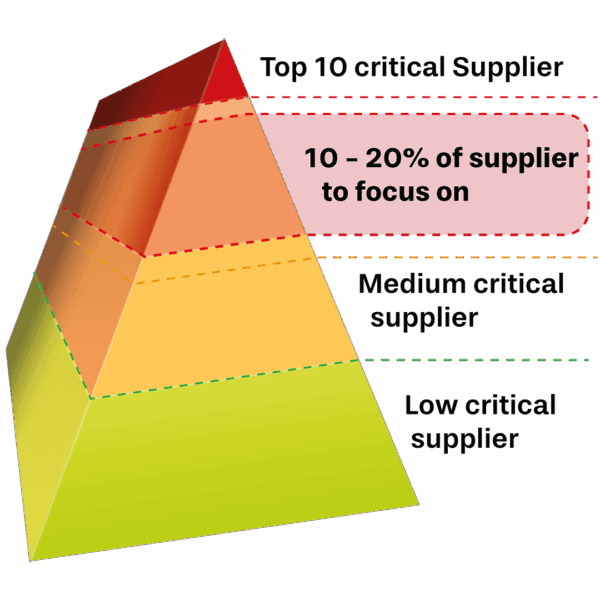
Thousands of processes and suppliers interact like tightly interlocked gears – or puzzle pieces. But what happens when one is missing? Focus is often placed on large, well-known suppliers. Yet the real risks hide where no one is looking – in the mid-tier, small vendors, or niche components.
This is where our approach to Cyber Risk Intelligence comes in: We reveal those hidden gaps before they become real threats.
Challenge:
In the automotive industry, supply chains are not just complex – they are vulnerable. And while the top 10 suppliers are usually under scrutiny, many risk-relevant partners remain under the radar. Especially the 10–20% ‘forgotten critical’ suppliers – not prominent but essential – pose a serious and often hidden threat.
The asvin Cyber Thread Intelligence Management Approach:
Our approach combines inside-out analysis (internal criticality, CSMS, self-assessments) with outside-in intelligence (darknet, OSINT, publicly reported incidents, ratings). Supported by a semantic LLM model and dynamic knowledge graph, this provides a real-time risk landscape across the entire supply chain.